Overview:
An abscess can be defined as the accumulation of puss which form within a tissue in any region of the body. Puss is a secretion, usually whitish-yellow, manufactured and released from the inflamed tissues in contact with bacterial or fungal infections.
The accumulation of puss within the capsule is termed an abscess.
Kidney abscess (renal abscess) forms a puss-filled capsule within the renal parenchyma. A kidney abscess is a severe and potentially life-threatening medical condition characterized by the formation of a pus-filled cavity within the kidney tissue. Typically arising from a bacterial infection, kidney abscesses can result from various underlying causes, such as urinary tract infections or the spread of bacteria through the bloodstream.
Pathophysiology of disease:
An abscess or kidney abscess is formed due to the body’s defensive system to prevent transmitting infection-causing agents to other body organs.
Infection-causing bacteria are responsible for destroying the nearby cells of the kidneys; in response to this, the body’s immune system releases different types of cytokines.
These cytokines initiate the inflammatory response, through which the increased number of white blood cells reaches the affected site along with the high regional blood flow.
The abscess is formed by the nearby healthy renal parenchyma cells and acts as a preventive measure to safeguard the neighboring cells from puss.
In most cases, renal abscesses at the renal cortical region are caused by the blood-borne transmission of bacteria from the extrarenal site of infection.
Abscesses originating near the cortico-medullary region result from UTIs and associated bacterial flora. These abscesses are more likely to perforate and spread across the renal capsule.
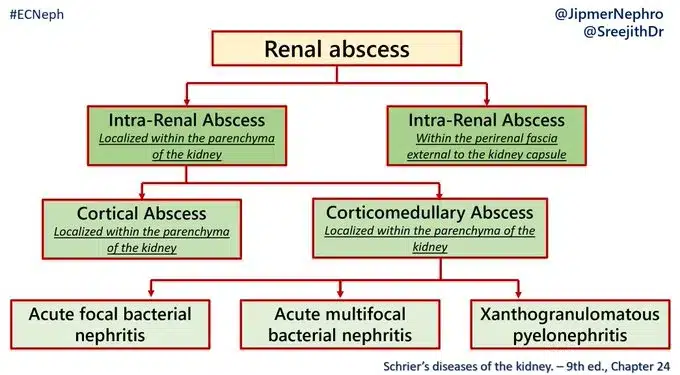
Types of Renal-associated abscesses:
Symptoms associated with Kidney Abscesses:
Symptoms associated with the kidney abscess are variable. Some of the significant signs and symptoms include:
- Dysuria (painful urination),
- Fever and chills,
- Low BMI,
- Hematuria (blood in urine),
- Hyperthermia (high fever),
- Lethargy,
- A general feeling of discomfort,
- Back pain,
- Loss of appetite,
- Abdominal pain radiates toward the groin and leg region.
Etiological factors contribute to Renal Abscesses:
The major etiological factors in the progression of kidney abscesses include:
- The most common causative agent for renal abscess is gram-negative bacteria like E. coli and Proteus. These bacteria initiate UTIs, which later cause abscesses if left untreated.
- Staphylococcus aureus is transmitted and causes infection through the hematogenous pathway.
- Prolonged and recurrent urinary tract infection.
- Tubular obstruction.
- Kidney calculus (nephrolithiasis).
- Ureteral trauma as a result of surgical procedures like ureteroscopy, etc.
- Backflow of urine towards kidneys because of weak detrusor muscle or congenital disability in trigonal muscles.
- Splenectomy.
Also explore: How does the Glomerulus filter the blood?
Diagnostic measures:
To diagnose the disorder, doctors prescribe various investigative tests along with the patient’s complete medical history and physical analysis.
Laboratory diagnostic tests that aid in the identification of underlying conditions include:
Blood tests:
- CBC (complete blood count) helps check the number of white blood cells in plasma.
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) is used to identify the estimate of infection found in the body.
- Blood culture is used to check the availability of pathogenic organisms in blood.
- CRP (C-reactive protein) is another important diagnostic tool for confirming inflammation elsewhere in the body.
- PT (prothrombin time) to identify the coagulation time.
- Blood gas testing (for sepsis).
Urine tests:
- Urinalysis is the chemical, physical and microscopic examination of urine. These aspects of analysis help check the presence of various compounds like crystals, puss cells, and bacteria, which are not present in normal circumstances.
- Urine culture is similar to blood culture and is used to identify the presence of bacteria in urine.
Radiological tests:
- X-ray (helpful to check the presence of stones in the kidney).
- Renal ultrasonography (KUB).
- Computed tomography (CT scan) contrast is considered most appropriate in imaging the renal abscess.
Treatment:
Treatment options always depend upon the severity and causative agent of the abscess. It is essential to find out the actual root cause of the disease so that further prognosis can be carried out.
Usually, the first line of treatment prescribed by nephrologists is antibiotics and other counter-act medications.
Sometimes, antibiotics alone are unable to correct the abscess. So, in such cases, surgical drainage and removal of puss exudate through the catheter is mandatory to cure the abscess.
IV-administrated antibiotics are given until the infection is gone.
Risk factors/Complications:
It is no doubt to say that an abscess involving the kidney remains a severe health concern if left untreated. Some of the complications accompanying it are:
- Septicemia
- CKD
- Renal Atrophy
- Renal failure
Relation between UTIs and Kidney Abscess concerning VUR:
- Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) is a pathological condition in which urine flows inversely from the urinary bladder to either one or both ureters and occasionally towards the kidneys.
- Untreated UTIs can lead to renal abscesses. The primary transmission route is ascending UTIs from the urinary bladder and vesicoureteral reflux (VUR).
- Cystourethrography or voiding sonography is used to diagnose the VUR. However, these processes are a little bit invasive.
- Accurate evaluation and prognosis of VUR are essential for understanding the surgical requirements for curing the ongoing infection and kidney damage.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, dealing with a kidney abscess can be a challenging experience, but timely diagnosis and appropriate medical intervention are crucial for a successful recovery. Paying attention to symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention, and following the prescribed treatment plan are essential. Individuals can overcome kidney abscesses and regain their health with the proper care and support. Open communication with healthcare professionals is necessary to manage this condition effectively. Overall, staying informed, seeking help when needed, and adhering to medical advice can pave the way for a smoother journey towards healing.
REFERENCES:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abscess
https://www.urology-textbook.com/renal-abscess.html
https://healthmatch.io/kidney-disease/what-is-a-kidney-abscess#management-and-treatment
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1341321X23001484

I enjoy what you guys are up too. Such clever work and exposure!
Keep up the wonderful works guys I’ve included you guys to my personal blogroll.
thank you
I have been browsing online more than 3 hours today, yet I never found any
interesting article like yours. It’s pretty worth
enough for me. Personally, if all website owners and
bloggers made good content as you did, the internet will be a
lot more useful than ever before.
thank you for your appreciation.